Cradle of democracy answer key sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. From ancient Athens to modern-day democratic models, this comprehensive guide unravels the intricate tapestry of democratic thought and practice, providing a captivating journey through the evolution of one of humanity’s most cherished ideals.
Prepare to embark on an intellectual odyssey as we delve into the cradle of democracy, tracing its historical roots, exploring its key principles, and examining the challenges and opportunities that shape its future. Whether you’re a history buff, a political science enthusiast, or simply curious about the foundations of modern society, this guide will provide you with a wealth of knowledge and insights.
Cradle of Democracy
The term “cradle of democracy” refers to a region or civilization where the principles and practices of democracy originated and developed.
Unlocking the secrets of democracy’s origins is a fascinating journey. To delve deeper into the “cradle of democracy answer key,” it’s worth exploring Empro Manufacturing v. Ball Co. , a legal case that sheds light on the complexities of corporate governance and accountability.
By examining this case, we gain valuable insights into the foundational principles that have shaped our democratic institutions, ultimately enriching our understanding of the “cradle of democracy answer key.”
Origins and Evolution of the Term
The term has its roots in ancient Greece, where the city-state of Athens is widely regarded as the birthplace of democracy. The Greek word “demokratia” (δημοκρατία) translates to “rule by the people,” reflecting the Athenian system of government, where citizens actively participated in decision-making through assemblies and elections.
The concept of democracy spread throughout the Greek city-states and later influenced the Roman Republic. During the Enlightenment period in Europe, the idea of democracy was revived and became a central theme in political thought, inspiring revolutions and the establishment of democratic governments around the world.
Medieval and Renaissance Influences on Democratic Thought
The democratic ideals of ancient Greece and Rome left an enduring legacy that influenced the development of democratic thought during the medieval and Renaissance periods. Medieval scholars and philosophers, such as Thomas Aquinas and Marsilius of Padua, drew inspiration from classical texts to explore concepts of popular sovereignty and the limits of monarchical power.
Role of Scholars and Philosophers
Medieval and Renaissance scholars played a pivotal role in shaping democratic principles. They studied and interpreted ancient Greek and Roman texts, extracting ideas that could be applied to their own societies. Through their writings and teachings, they disseminated these ideas, fostering a climate of intellectual inquiry and debate.
For example, Thomas Aquinas argued that political authority should be derived from the consent of the governed, while Marsilius of Padua emphasized the importance of popular sovereignty and the separation of church and state.
Enlightenment and the Rise of Modern Democracy: Cradle Of Democracy Answer Key

The Enlightenment, an intellectual movement of the 18th century, played a pivotal role in shaping the foundations of modern democratic thought and practice. Enlightenment philosophers challenged traditional authorities and promoted reason, individual rights, and popular sovereignty.
Key ideas and principles espoused by Enlightenment thinkers included:
- Natural rights: The belief that all individuals possess inherent and inalienable rights, such as life, liberty, and property.
- Social contract theory: The idea that government is based on a voluntary agreement between citizens and the state, with the consent of the governed being essential.
- Separation of powers: The division of government into different branches, such as the executive, legislative, and judicial, to prevent the concentration of power in any one entity.
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1775-1783) was a pivotal event in the development of modern democracy. Inspired by Enlightenment ideals, the American colonists declared independence from British rule and established a new nation based on the principles of liberty, equality, and self-government.
Key features of the American Revolution included:
- Declaration of Independence: A formal statement of the colonists’ grievances against British rule and their assertion of natural rights.
- Articles of Confederation: The first constitution of the United States, which established a loose confederation of states.
- U.S. Constitution: A landmark document that established a strong central government with a system of checks and balances.
French Revolution, Cradle of democracy answer key
The French Revolution (1789-1799) was another significant moment in the rise of modern democracy. Influenced by Enlightenment ideas, the French people overthrew the monarchy and established a republic based on the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Key events of the French Revolution included:
- Storming of the Bastille: A symbolic event that marked the beginning of the revolution and the collapse of the monarchy.
- Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen: A document that enshrined the fundamental rights of all citizens.
- Reign of Terror: A period of political violence and instability that followed the revolution.
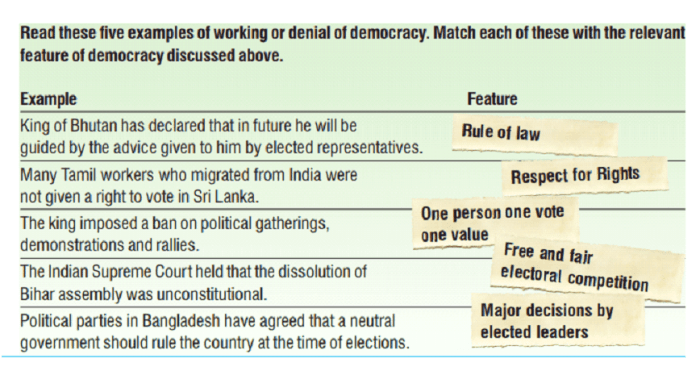
Challenges and Criticisms of Democracy
Democracy has faced numerous challenges and criticisms throughout history. One major concern is the tension between majority rule and minority rights. Majority rule is a fundamental principle of democracy, as it ensures that the will of the people is reflected in government decisions.
However, it can also lead to the suppression of minority views and interests. To address this tension, democratic societies often implement mechanisms such as constitutional protections, minority representation, and judicial review to safeguard the rights of minorities.Another criticism of democracy is that it can lead to mob rule or the tyranny of the majority.
This occurs when the majority uses its power to oppress or silence dissenting voices. To prevent this, democracies rely on institutions such as independent courts, free press, and civil society organizations to provide checks and balances on the power of the majority.Additionally,
some critics argue that democracy is inefficient and slow, as it requires consensus-building and compromise. They contend that authoritarian regimes can make decisions more quickly and effectively. However, proponents of democracy argue that the benefits of public participation, transparency, and accountability outweigh the potential inefficiencies.Finally,
democracy requires an informed and engaged citizenry. Without an educated and civically engaged population, democracies can become vulnerable to manipulation, corruption, and apathy. To address this challenge, democratic societies invest in education, civic education programs, and opportunities for public participation to foster an active and informed citizenry.
The Future of Democracy

The 21st century presents both challenges and opportunities for democracy. Globalization, technology, and social movements are reshaping the political landscape, creating new opportunities for citizen participation and accountability, but also raising concerns about the erosion of traditional democratic institutions.
Technology and Democracy
Technological advancements, such as social media and data analytics, have the potential to enhance democratic processes. They can facilitate civic engagement, increase transparency, and empower citizens to hold their leaders accountable. However, these same technologies can also be used to spread misinformation, manipulate public opinion, and undermine democratic institutions.
Globalization and Democracy
Globalization has led to increased interdependence and interconnectedness, creating new challenges for democratic governance. The flow of goods, capital, and people across borders can strain traditional democratic institutions and make it more difficult to address global issues such as climate change and economic inequality.
Social Movements and Democracy
Social movements, often fueled by social media and technology, have emerged as a powerful force for change. They have the potential to challenge the status quo, raise awareness of important issues, and demand accountability from governments. However, social movements can also be divisive and lead to political polarization.
The Role of Citizens and Civil Society
The future of democracy depends on the active participation of citizens and civil society organizations. Citizens need to be informed, engaged, and willing to hold their leaders accountable. Civil society organizations play a crucial role in promoting democratic values, advocating for social justice, and holding governments to account.
FAQ Compilation
What is the origin of the term “cradle of democracy”?
The term “cradle of democracy” has its roots in ancient Greece, where the concept of citizen participation in government first emerged.
What were the key principles of Athenian democracy?
Athenian democracy was based on the principles of equality, freedom of speech, and majority rule, with citizens directly participating in decision-making through assemblies and courts.
How did Roman law contribute to the development of democracy?
Roman law established the concept of due process and equal protection under the law, which became fundamental principles of modern democratic systems.
What was the impact of the Enlightenment on democratic thought?
Enlightenment philosophers emphasized the importance of reason, individual rights, and popular sovereignty, which laid the foundation for modern democratic revolutions.
What are the different models of democracy that exist today?
Contemporary democratic models include liberal democracy, social democracy, and participatory democracy, each with its own unique characteristics and strengths.
