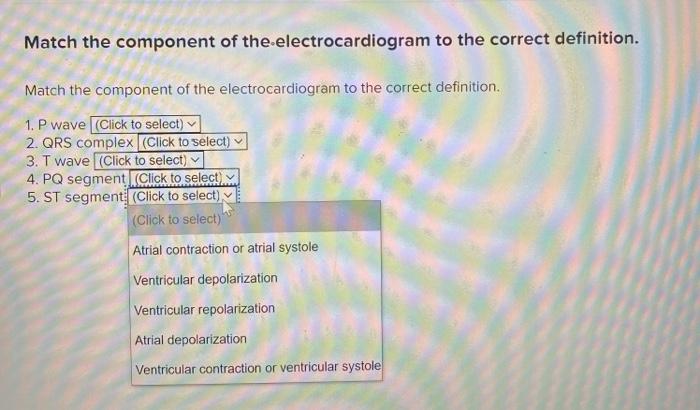
Match the component of the electrocardiogram to the correct definition. – Match the Electrocardiogram Component to its Correct Definition takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authority, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. As we delve into the intricacies of the electrocardiogram, we will uncover the significance of each component, empowering you with the knowledge to interpret these vital signals with precision.
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart. It is a non-invasive test that can provide valuable information about the heart’s rhythm, rate, and electrical conduction. The ECG is composed of several distinct components, each with its own unique significance.
Understanding these components is essential for accurate ECG interpretation.
Electrocardiogram Components: Match The Component Of The Electrocardiogram To The Correct Definition.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart. It is used to diagnose a wide range of cardiac conditions, including arrhythmias, conduction disturbances, and myocardial infarction.
An ECG consists of several distinct components, each of which represents a specific electrical event in the heart.
ECG Component Definitions
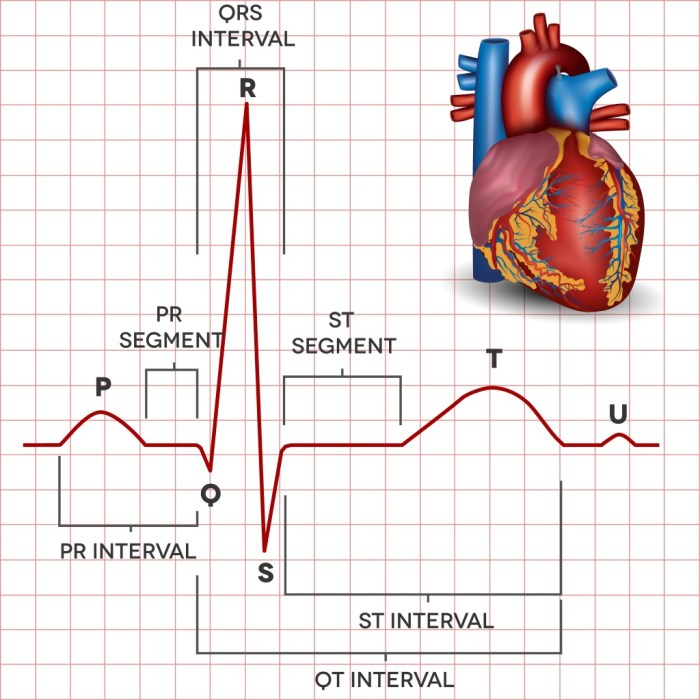
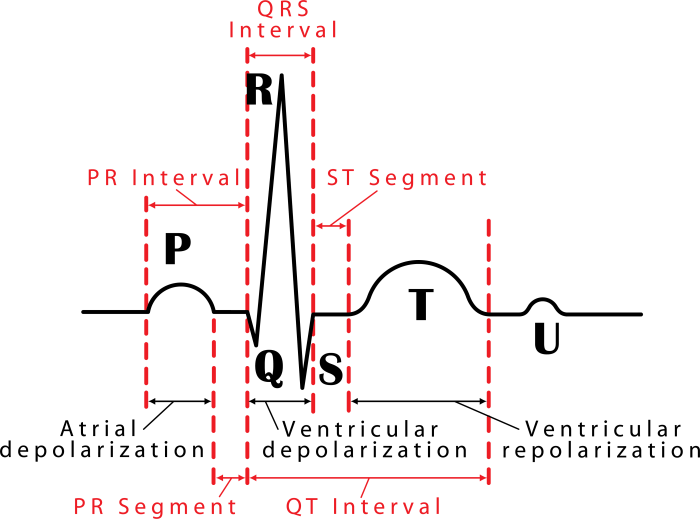
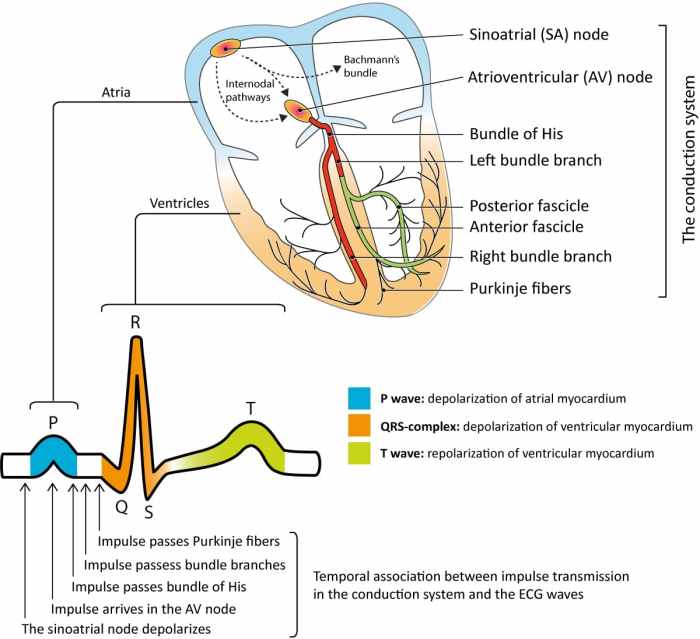
- P wave:Represents the depolarization of the atria.
- QRS complex:Represents the depolarization of the ventricles.
- T wave:Represents the repolarization of the ventricles.
- U wave:Represents the repolarization of the Purkinje fibers.
- PR interval:Represents the time from the onset of the P wave to the onset of the QRS complex.
- QT interval:Represents the time from the onset of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave.
ECG Component Functions, Match the component of the electrocardiogram to the correct definition.
Each ECG component has a specific function in the cardiac cycle.
- P wave:Indicates the onset of atrial contraction.
- QRS complex:Indicates the onset of ventricular contraction.
- T wave:Indicates the end of ventricular contraction.
- U wave:Indicates the repolarization of the Purkinje fibers.
- PR interval:Indicates the time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
- QT interval:Indicates the time it takes for the ventricles to repolarize.
ECG Component Abnormalities
Abnormalities in the ECG components can indicate a variety of cardiac conditions.
- P wave abnormalities:Can indicate atrial enlargement, atrial arrhythmias, or electrolyte imbalances.
- QRS complex abnormalities:Can indicate ventricular hypertrophy, bundle branch blocks, or myocardial infarction.
- T wave abnormalities:Can indicate myocardial ischemia, electrolyte imbalances, or drug toxicity.
- U wave abnormalities:Can indicate hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia.
- PR interval abnormalities:Can indicate atrial arrhythmias or conduction disturbances.
- QT interval abnormalities:Can indicate electrolyte imbalances, drug toxicity, or genetic disorders.
ECG Interpretation
ECG interpretation involves analyzing the ECG components to identify any abnormalities.
By understanding the function and significance of each ECG component, clinicians can accurately diagnose and manage a wide range of cardiac conditions.
User Queries
What is the P wave?
The P wave represents the electrical depolarization of the atria.
What is the QRS complex?
The QRS complex represents the electrical depolarization of the ventricles.
What is the T wave?
The T wave represents the electrical repolarization of the ventricles.