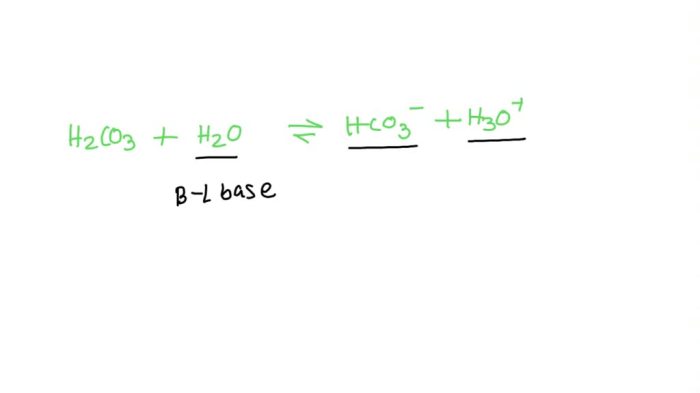Complete the 𝐾a2 expression for h2co3 in an aqueous solution. embarks on an illuminating journey into the realm of chemistry, unraveling the intricacies of Ka2 and its profound influence on the dissociation of H2CO3 in aqueous environments. This discourse delves into the factors that modulate Ka2, the experimental methodologies employed to determine its value, and the diverse applications of Ka2 across scientific disciplines.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of Ka2, we uncover its pivotal role in shaping the equilibrium of carbonic acid in aqueous solutions. By elucidating the relationship between Ka2 and the concentrations of H+, HCO3-, and CO32- ions, we gain a profound understanding of the behavior of this crucial chemical system.
Ka2 of Carbonic Acid (H2CO3) in Aqueous Solution: Complete The 𝐾a2 Expression For H2co3 In An Aqueous Solution.

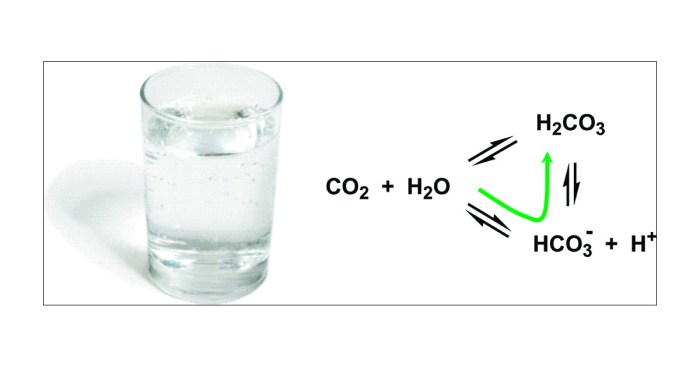
Carbonic acid (H2CO3) is a weak acid that dissociates into hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) in aqueous solution. The extent of this dissociation is quantified by the second dissociation constant (Ka2), which is an important parameter in understanding the behavior of carbonic acid in various chemical and biological systems.
Definition of Ka2, Complete the 𝐾a2 expression for h2co3 in an aqueous solution.
Ka2 is defined as the equilibrium constant for the second dissociation of carbonic acid:“`H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H+(aq) + HCO3-(aq)“`It represents the ratio of the concentration of hydrogen ions multiplied by the concentration of bicarbonate ions to the concentration of undissociated carbonic acid at equilibrium.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of Ka2 in understanding the dissociation of H2CO3?
Ka2 is the second dissociation constant of carbonic acid (H2CO3), and it quantifies the extent to which HCO3- ions dissociate further to form CO32- ions in aqueous solutions. This dissociation process is crucial for understanding the behavior of carbonic acid in various chemical and biological systems.
How does temperature affect the value of Ka2 for H2CO3?
Temperature has a significant impact on the value of Ka2 for H2CO3. As temperature increases, the dissociation of HCO3- ions into CO32- ions becomes more favorable, leading to an increase in the value of Ka2.
What experimental methods are commonly used to determine the value of Ka2 for H2CO3?
The value of Ka2 for H2CO3 can be determined using various experimental methods, including potentiometry, conductometry, and spectrophotometry. These methods involve measuring the pH, conductivity, or absorbance of H2CO3 solutions under controlled conditions.