Identify each account as an asset liability or equity – In the realm of accounting, the ability to identify each account as an asset, liability, or equity is paramount. This distinction forms the foundation of financial reporting and provides crucial insights into a company’s financial health. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental differences between these account types, offering practical methods for their identification and highlighting their significance in the financial statements.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the characteristics that distinguish assets from liabilities, unravel the nature of equity accounts, and delve into the intricacies of balance sheet presentation. By the end of this exploration, you will possess a deep understanding of account classification, empowering you to navigate the complexities of financial reporting with confidence and precision.
Account Classification: Assets, Liabilities, and Equity

In accounting, accounts are classified into three main categories: assets, liabilities, and equity. These categories represent different types of financial resources and obligations.
Assets
Assets are economic resources owned by a company that have value and can be converted into cash. They represent the company’s resources that can be used to generate future economic benefits.
- Cash
- Accounts receivable
- Inventory
- Property, plant, and equipment
Liabilities
Liabilities are debts or obligations that a company owes to others. They represent the company’s financial responsibilities and the amounts that it must pay to creditors.
- Accounts payable
- Notes payable
- Bonds payable
- Taxes payable
Equity
Equity represents the ownership interest in a company. It is the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities. Equity is owned by the company’s shareholders.
- Common stock
- Preferred stock
- Retained earnings
Identifying Accounts as Assets or Liabilities: Identify Each Account As An Asset Liability Or Equity
Characteristics of Assets
Assets typically have the following characteristics:
- Controlled by the company
- Expected to provide future economic benefits
- Acquired through a transaction or event
Characteristics of Liabilities
Liabilities typically have the following characteristics:
- Present obligation of the company
- Expected to result in an outflow of economic resources
- Incurred through a transaction or event
Methods for Identifying Assets or Liabilities
To determine whether an account represents an asset or a liability, consider the following questions:
- Does the company control the resource?
- Will the resource provide future economic benefits?
- Is there a present obligation to pay or perform?
Identifying Equity Accounts
Nature of Equity Accounts, Identify each account as an asset liability or equity
Equity accounts represent the ownership interest in a company. They are not liabilities because the company does not have an obligation to repay them.
Examples of Equity Accounts
Common equity accounts include:
- Common stock
- Preferred stock
- Retained earnings
Role of Equity in Financial Statements
Equity is a key component of the balance sheet, which shows the financial position of a company at a specific point in time. Equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities.
Balance Sheet Presentation
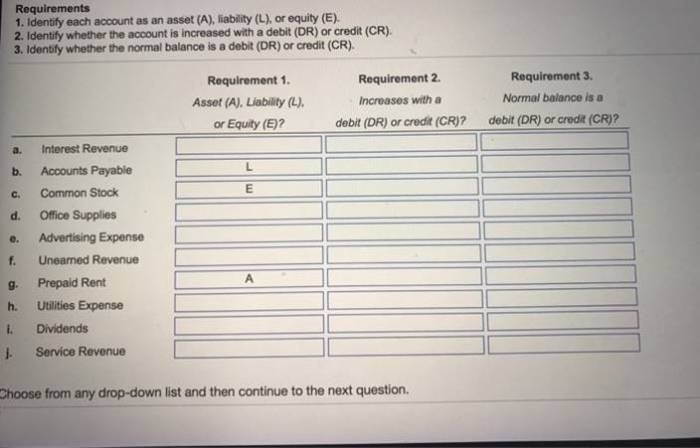
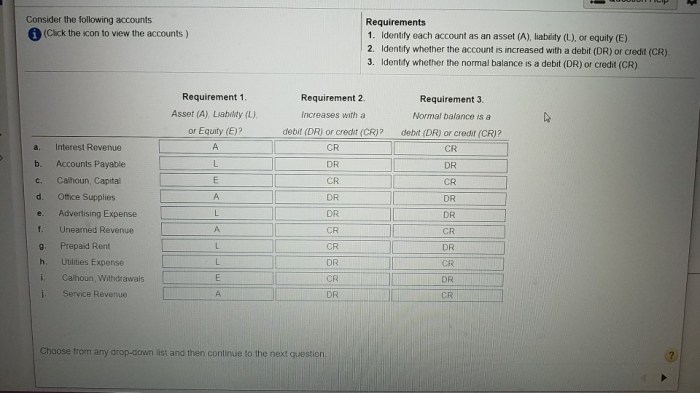
The following table shows the classification of accounts on the balance sheet:
| Assets | Liabilities | Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | Accounts payable | Common stock |
| Accounts receivable | Notes payable | Preferred stock |
| Inventory | Bonds payable | Retained earnings |
| Property, plant, and equipment | Taxes payable |
Top FAQs
What is the primary difference between an asset and a liability?
Assets represent economic resources controlled by a company, while liabilities are obligations that must be fulfilled in the future.
How can I determine if an account is an equity account?
Equity accounts reflect the ownership interest in a company and typically include retained earnings, common stock, and other contributed capital.
What is the significance of the balance sheet in account classification?
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, categorizing accounts as assets, liabilities, or equity.